Have you ever thought about if Jewish dietary laws and Muslim dietary rules can mix? With over 5 million Muslims in the U.S., many wonder: can Muslims eat kosher? This question looks into how Kosher and Halal practices work together. It also questions how dietary laws affect our cultural identity.
With about 1.6 billion Muslims worldwide, knowing how these traditions meet is key. In this article, we’ll dive into Jewish and Muslim dietary laws. We’ll see what it means to eat kosher food from an Islamic view.
Understanding Kosher and Halal Dietary Laws
Dietary laws in Judaism and Islam are key to cultural practices and what people choose to eat. Kosher laws, known as Kashrut, guide Jewish dietary habits. They tell what’s okay to eat and how it should be prepared. These rules come from the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud.
Overview of Kosher Laws
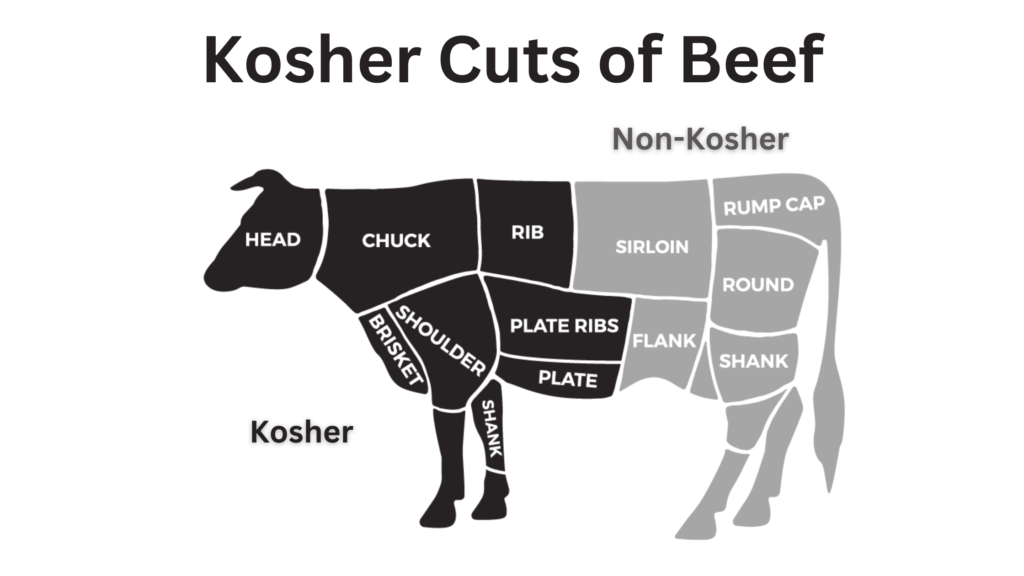
Kashrut puts foods into three groups: Meat (fleischig), Dairy (milchig), and Pareve. Jews can’t eat certain animals, parts of animals, or mix meat and dairy. Kosher laws require food to be checked by rabbis to meet strict standards. Different Jewish groups have their own rules, like Ashkenazi Jews avoiding lamb during Passover.
To stay kosher, products must be clean and kept separate. This helps keep them kosher.
Overview of Halal Laws
Halal laws tell Muslims what foods they can eat, based on the Quran. Halal laws also cover other products, like saying what’s haram— forbidden foods, like alcohol and pig products. Halal meat must be prepared with care for animal welfare and humane slaughter.
Halal allows meat from Christians or Jews if the butcher says Allah’s name during slaughter. Both halal and kosher laws avoid mixing with forbidden substances.
Key Differences Between Halal and Kosher
Halal and Kosher dietary laws have unique features tied to their religious roots. They guide what foods are okay or not okay to eat.
Slaughter Methods
Halal and kosher slaughter focus on treating animals kindly but have different rituals. Halal slaughter cuts the animal’s jugular vein while saying the name of Allah. This aims to lessen suffering and honor the life taken. Kosher slaughter doesn’t need a prayer before the animal is killed but also ensures the animal’s comfort. Both methods follow strict rules to meet religious duties.
Permissible and Forbidden Foods
Halal and kosher diets have big differences in what foods are allowed or not. Halal bans pork, reptiles, and birds of prey, and also blood and alcohol. Kosher also says no to pork and some animals like horses and rabbits. Kosher also avoids certain animal parts like the sciatic nerve. Knowing these rules helps people choose what to eat wisely.
Can Muslims Eat Kosher Products?
Muslims often wonder if they can eat Kosher products. Some Kosher foods seem okay, but not all follow Halal rules. So, Muslims need to check labels carefully to make sure they’re okay to eat.
The American Halal Foundation says it’s key to check if Kosher meat and foods are Halal certified. Not all Kosher products are Halal. Some might not be allowed because of how they’re made or what’s in them.
Before eating Kosher foods, Muslims should look for a Halal stamp. It’s important to focus on what’s Halal. With most U.S. products not certified Halal, being careful is a must.
Knowing the difference between Kosher and Halal can guide Muslim shoppers. It helps them pick foods that fit their dietary laws. This way, they can enjoy a wider variety of foods while staying true to their beliefs.
Halal Certification versus Kosher Certification
Halal and Kosher certifications have their own rules and groups that check them. These groups make sure foods in the US meet their standards. This helps us understand how these foods are available in the market.
Certification Organizations
Halal food is checked by groups like the Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America. They make sure foods follow Islamic dietary laws. Kosher food has its own groups that follow the Torah and Talmud. These groups check if food meets Kashrut laws, from where ingredients come to how they are made.
Market Availability of Halal and Kosher Foods
Kosher foods are easy to find in stores and restaurants in the US. They appeal to Jewish people and others who want these products. Halal foods are harder to find, but more people are looking for them. This has made certification groups work harder to offer more Halal and Kosher options.
The Role of Alcohol in Kosher and Halal Foods
Alcohol is a big topic in Kosher and Halal diets. It’s important for people who follow these diets to know how alcohol is treated. This helps them make the right food choices.
Alcohol in Kosher Products
In kosher rules, some alcohols are okay if they’re made and checked the right way. Wine and grape juice have extra rules because they’re important in rituals. Kosher products with alcohol can’t touch anything not kosher.
This means people following kosher have to check all ingredients, especially in drinks. They make sure everything follows their religious laws.
Alcohol and Halal Guidelines
For Halal, alcohol is a big no-no. It’s called haram, or forbidden. This means no food or drink with alcohol is allowed. This includes many foods like desserts and flavored drinks.
Drinking intoxicants like alcohol is not allowed. So, it’s key to know what’s in your food and drinks. Muslims need to be careful and informed to follow their diet rules.
You may also be interested in:
Similarities Between Jewish and Muslim Dietary Practices
Jewish and Muslim dietary laws share many similarities in dietary laws. They both have strict rules about food, shaping their cooking traditions. Both faiths forbid eating pork, making it a key rule. They also agree on the blood prohibition, requiring animals to be bled completely during slaughter.
Common Prohibitions: Pork and Blood
Islamic and Jewish diets ban many animals like carrion, insects, rodents, and blood. This shows their shared belief in clean food and what’s okay to eat. They only allow healthy animals for slaughter, following their dietary laws. For more details, check out the comparison of Islamic and Jewish diets.
Importance of Cleanliness and Preparation
Cleanliness is key in preparing and eating food in both cultures. They have strict ways of slaughtering animals to keep their food clean. For example, halal meat uses the dhabiha method with prayers, while kosher meat goes through shechita. This highlights the importance of food cleanliness in their beliefs.
Challenges for Muslims Seeking Kosher Products
Muslims often find it hard to find Kosher products that fit their diet. They look for Halal certified options. In the U.S., more Halal supervision agencies have started to help the growing Muslim community. But, only a small number of products are Halal certified, making choices limited for consumers.
Availability of Halal Certified Options
Only 37% of Muslims buy only Halal-certified products. Many look for other options that might not be clearly marked as Halal. Islamic Services of America works with many companies to help follow Halal rules. This helps make Halal products easier to find, but finding the right brands or food types can still be hard.
Understanding Packaging Labels
People have to be careful with packaging labels to make sure their food is okay for their diet. Labels with “Kosher” or symbols might not always mean the product is Halal. For grape products, special supervision is needed because they’re often made in Kosher lines. Cleaning equipment also has different rules for Halal, making it tough for Muslims to know if their food is right.
The Cultural Significance of Dietary Laws
Dietary laws are key in shaping culture in Jewish and Muslim communities. They go beyond just food choices, becoming a big part of religious identity. Following kosher and halal rules helps people feel connected to their communities.
Impact on Religious Identity
Following dietary laws strengthens community bonds, deeply linked to religious identity. It shows a deep commitment to faith and tradition. For Jews, kosher laws connect them to Jewish history and spirituality.
For Muslims, eating halal shows a strong dedication to Islamic teachings. This bond makes them feel part of their faith community.
Culinary Traditions and Practices
Culinary traditions from dietary laws add to cultural heritage. Kosher and halal food are central to many traditional recipes and cooking ways. Special dishes and rituals bring people together during holidays.
These traditions keep evolving, showing the deep cultural value of dietary laws. As more people choose kosher and halal foods, these practices shape meals and celebrations.
Interfaith Dining: Kosher and Halal Friendly Restaurants
The world of interfaith dining is changing fast. It’s bringing people together through shared love for food. Kosher and Halal restaurants now serve both Jewish and Muslim diners. They create a place where everyone can feel welcome.
These restaurants offer meals that follow both Kosher and Halal rules. This makes dining more enjoyable and helps people from different cultures learn from each other. It shows how important it is to respect each other’s beliefs at the dinner table.
Now, some places are trying new things like “Interfaith Meat.” This idea combines Kosher and Halal ways of eating. It shows how restaurants can cater to more people’s dietary needs, making food more inclusive.
Offering Kosher and Halal options is a big step towards welcoming everyone. It lets communities share meals and talk about their faith and food traditions. This kind of togetherness is powerful.
Conclusion: Navigating Food Choices
In today’s world, making food choices is more important than ever. People who care about their diets can look into Kosher and Halal options. These choices guide many people in what they eat.
Learning about the values behind these choices shows us how they both care for animals. Kosher and Halal have their own rules, but they both build community and make sure food is safe to eat.
When we think about what we eat, knowing about food labels is key. This helps us make choices that match our values. Now, we’re seeing new trends like eco-halal and Jewish food ethics that focus on being kind to the planet.
Choosing what to eat is more than just eating. It’s about respecting different cultures and traditions. It’s about seeing the world through the food we eat.
Further Exploration: Resources and Organizations
For those wanting to learn more about Kosher and Halal dietary laws, many resources and organizations are available. They offer detailed information and help with food choices based on beliefs. These groups make it easier to follow dietary laws.
Important organizations like the Orthodox Union and the Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America are key. They check products and teach people about dietary laws. Their websites are great places to learn about Kosher and Halal standards.
Academic resources and events, like the Winter Term Kosher-Halal Co-op, also help. They bring together Jewish and Muslim communities. These programs show how these groups work together to follow their dietary laws and respect each other. Joining these events can teach you more about dietary laws and how they work.
FAQ
Can Muslims eat Kosher food?
What are the main differences between Halal and Kosher dietary laws?
What are the alcohol guidelines in Halal and Kosher dietary practices?
How do I identify Halal certified products?
Are there similarities between Jewish and Muslim dietary laws?
How do dietary laws impact religious and cultural identity?
What are some challenges Muslims face when seeking Kosher products?
Are there restaurants that cater to both Kosher and Halal dietary needs?
Where can I find resources for understanding Kosher and Halal dietary laws?

Embracing Faith, One Insight at a Time!
The teachings of the Quran have always guided my path. With a deep passion for Islamic knowledge, I strive to blend the wisdom of tradition with the relevance of today, making the timeless messages of Islam accessible and meaningful for everyone.
Muslim Culture Hub is my platform to share historical insights and thought-provoking articles, exploring both well-known and lesser-discussed aspects of Islamic culture and beliefs. My mission is to create an inclusive online space where everyone can learn, strengthen their faith, and connect with the profound message of Islam.
Join the journey!
May peace be upon you.








